AR: Opening Doors to Immersive Experiences
Within the rapidly changing field of technology, augmented reality (AR) has become a revolutionary instrument that can turn the ordinary into the extraordinary. Virtual elements and real-world events interact in a hybrid environment created by this unique technology that combines the best elements of the digital and physical worlds. Augmented Reality (AR) enhances the reality you would normally see by overlaying layers of digital information, in contrast to virtual reality (VR), which requires users to occupy a digital world. There are countless opportunities to improve user experience (UX) across various disciplines thanks to augmented reality’s unique ability to blend digital material with the real environment.
In today’s digital age, brands must design strategies that resonate with their customers. Augmented Reality has become a powerful tool to achieve this goal.
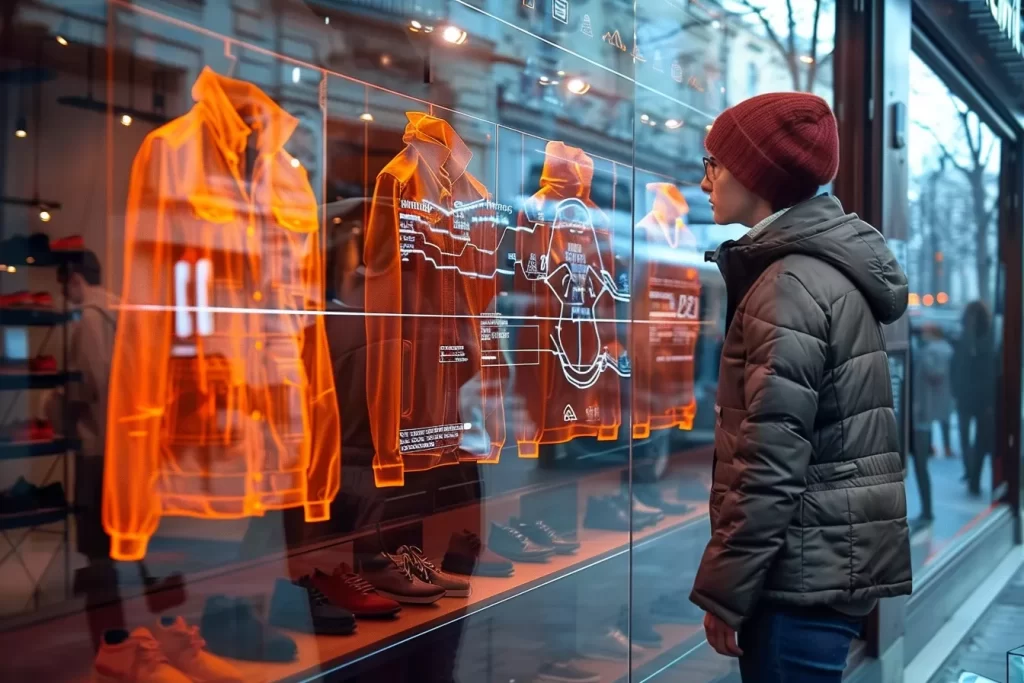

Development of AR in User Experience Design
It’s amazing how far augmented reality has come from a novel notion to becoming a major force in user experience design. At first, augmented reality (AR) was mainly used in entertainment and games. Games like Pokémon GO, which went viral around the world, took players to a new level of engagement. However, sectors as diverse as retail, healthcare, education, and more quickly saw its potential to completely revolutionize user experiences.

Customers can use augmented reality (AR) in retail, for example, to see things in the store before purchasing them. Consider how easily you can visualize, through your smartphone screen, the arrangement of a piece of furniture in your living room, or the way a certain pair of sunglasses fits your face. As a result, customers are more satisfied and return rates decrease, while greatly improving the online shopping experience by reducing the level of uncertainty.
-
Shaping the Future of Healthcare and Education
utilization of historical events to virtual dissection of frogs in biology classes. visualization of historical events to virtual dissection of frogs in biology classes. AR provides students with immersive and engaging learning experiences by bringing complicated concepts to life in educational environments. AR increases accessibility and participation in learning, from 3D visualization of historical events to virtual frog dissection in biology classes.
AR has the potential to completely transform patient care and medical education. To improve precision and results, surgeons can now employ augmented reality (AR) to visualize internal organs and muscles during surgery or training. AR apps can also help patients with complicated treatment plans by assisting with rehabilitation exercises or visualizing operations, making medical material easier to understand and less frightening.
-
Improve Everyday Experiences
In addition to these fields, augmented reality is permeating all aspects of our daily existence and improving our interactions with the environment. To make it easier to navigate strange places, navigation apps use augmented reality (AR) to overlay directions over the real landscape. Using AR, museums and historical sites can enhance the tourist experience by adding interactive elements and additional layers of information to their exhibits.
There has been a movement towards more immersive and participatory user experiences as a result of the integration of AR into numerous aspects of life. AR provides a more personalized and engaging method of interacting with material by bridging the gap between the digital and physical worlds, enhancing our impression of reality.
Discover how to innovate and realign brand strategies for Gen Z Market:

Exploring Augmented Reality: Tech, Tools, and Design Challenges
Understanding the technological framework that allows augmented reality (AR) to so easily combine digital and real-world data is essential as we delve deeper into this fascinating field. This integration incorporates advanced technology and design ideas that ensure a fluid, immersive, and interactive experience; It goes beyond simply overlaying images over real-world views. Furthermore, as developers and designers explore this uncharted territory, they encounter a different set of difficulties that test the limits of their imagination and technological ingenuity.
Fundamentals of AR experiences
Three essential technologies—computer vision, 3D rendering, and real-time data processing—are at the heart of any augmented reality system. Through the use of computer vision, machines can recognize surfaces, objects, and spatial connections in their surroundings by interpreting and comprehending the data that is collected by the camera. Accurately putting digital items in the actual environment requires this understanding.
These virtual things come to life using 3D rendering, which produces realistic or stylized images that seem to occupy our actual area. These things may interact visually coherently with physical objects, throw shadows, reflect light, and enhance the appearance of reality because of the complexity of contemporary rendering engines.
When the user or environment changes, real-time data processing ensures that digital material is updated instantly. Any lag or inconsistent performance will undermine user immersion and serve as a constant reminder that the experience is fake, making responsiveness essential to preserving the appearance of realism.
Tools of the Trade
Developers use a set of platforms and tools that simplify the process of developing, testing, and launching AR applications to produce AR experiences. At the forefront are powerful frameworks for creating augmented reality (AR) applications that can track the environment, identify surfaces, and understand lighting conditions to realistically position and render digital elements: ARKit for iOS and ARCore for Android.
Additionally, game engines with powerful visual and physics engines, such as Unity and Unreal Engine, are essential for the development of augmented reality. Using these technologies, developers can design intricate virtual landscapes and objects that can interact in sophisticated ways with the real world, expanding the possibilities of augmented reality experiences.
How to Deal with Design Obstacles
Designers must reconsider conventional user interfaces and interactions in light of the particular problems posed by designing for augmented reality. The user’s comfort and safety are important factors to take into account because augmented reality experiences frequently call for users to move around or focus on different areas of their surroundings. It is crucial to make sure that these interactions do not cause bodily pain or pose a safety risk.
Developing intuitive interactions in a setting where conventional design signals might not be applicable presents another difficulty. Because augmented reality (AR) integrates user interface components into the physical environment, designers have to figure out how to make interactions seem intuitive and natural. Using gestures, voice instructions, or contextual signals to lead the user through the experience without being overbearing might be one way to do this.
Explore the significance of sensory branding:
And last, there’s the accessibility issue. Designing AR experiences with inclusivity in mind means considering the diverse needs and capacities of users. Designing for people with physical, visual, or aural disabilities is part of this since it guarantees that AR technology improves experiences for all users.
know more about the philosophy behind accessibility in design:

The Broader Impact of Augmented Reality and Ethical Considerations
As we continue to explore how augmented reality (AR) might revolutionize the user experience, we must address the wider ramifications and ethical issues surrounding this quickly developing technology. To provide a thorough grasp of augmented reality’s future, this last section of our investigation into how AR is changing user interactions not only emphasizes the impact on society but also delves into the complex issues of privacy, data security, and the digital divide.
AR’s Effect on Society
Beyond the experiences of individual users, augmented reality’s capacity to superimpose digital data onto the actual environment has far-reaching ramifications. Its incorporation into urban planning, healthcare, and educational resources can improve learning results, democratize information access, and raise the standard of living. For example, by offering visual and interactive learning resources that adjust to different learning styles, augmented reality (AR) can increase accessibility to education for students with diverse requirements.
Explore the methods that can help you include consumer psychology in your brand strategy:

Furthermore, AR has the power to completely transform emergency response and public safety. AR can be critical to crisis management by giving first responders instantaneous information about their surroundings or assisting people in finding safe pathways during emergencies.
Getting Around Ethical Issues
AR raises difficult ethical questions, as does any technology that conflates the digital and physical domains. With AR apps that record and superimpose data on real-world surroundings, privacy becomes a major problem. Ensuring user experience without compromising privacy rights is a difficult balance that calls for strict data protection protocols and open user consent procedures.
Furthermore, as AR apps frequently need access to sensitive data, such as location information and personal identifiers, data security becomes a critical concern. It is essential to protect this data from illegal access and breaches to preserve user confidence and the integrity of augmented reality systems.
The possibility that AR would widen the digital gap is another ethical concern. As augmented reality technologies develop, there’s a chance that these breakthroughs will only help people who can afford the newest gadgets and high-speed internet. To ensure that everyone benefits equally from these developments, it will take coordinated efforts to lower the cost and increase the accessibility of augmented reality technology.

The Future of AR: A Balanced Approach
Future directions for augmented reality in user experience design show a great deal of promise and responsibility. It is critical to take a balanced approach that takes into account not just the scientific improvements but also the societal effect and ethical implications of augmented reality (AR), especially as designers, developers, and stakeholders continue to push the frontiers of what is possible with this technology.
It is imperative to ensure that augmented reality technologies augment human experiences while respecting privacy, security, and fairness. Technologists, ethicists, politicians, and the general public must continue to communicate to create a future in which AR technologies are created and applied advantageously, responsibly, and inclusively.

Navigating the Future of AR: Charting the Course Ahead
With its ability to offer a glimpse into a future in which the distinctions between the digital and physical worlds become increasingly blurred, augmented reality stands as a beacon of innovation in the user experience.
The process of incorporating augmented reality (AR) into our daily lives and communities is ongoing and requires critical evaluation of how the technology can impact social justice, privacy, and security. We can fully utilize augmented reality to create immersive and engaging experiences that respect our collective rights and values by adopting a forward-thinking strategy that places a high priority on inclusion and responsible innovation.
The future of augmented reality (AR) is not just about the technology itself, but also how we choose to shape it as we stand on the cusp of this new frontier in user experience. We can ensure that augmented reality improves our lives in meaningful, safe, and inclusive ways by working together, being creative, and practicing ethical stewardship. This will open doors to areas of possibilities and wonders hitherto unexplored in the digital age.
Learn how to maintain a strong brand identity:



